When it comes to powering vehicles, diesel and gasoline are the two most common fuel types. Each uses a different fuel system designed specifically to handle the unique properties of the fuel. Understanding the differences between diesel and gasoline fuel systems can help you appreciate how engines operate and why certain vehicles perform the way they do. Diesel vs. Gasoline Fuel Systems
How Gasoline Fuel Systems Work
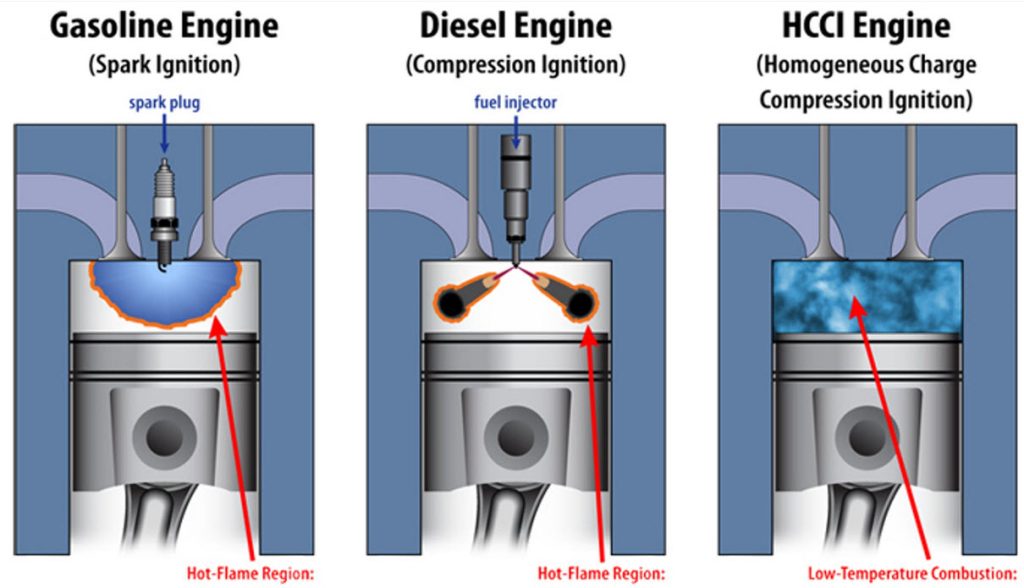
Gasoline engines typically use fuel injection systems that spray a fine mist of gasoline into the engine’s intake manifold or combustion chamber. The fuel mixes with air and is ignited by spark plugs, producing the power needed to move the vehicle.
Key components of a gasoline fuel system include:
- Fuel Tank
- Electric Fuel Pump
- Fuel Filter
- Fuel Injectors or Carburetor
- Spark Plugs
Gasoline fuel systems operate under relatively lower pressures compared to diesel systems. They rely on spark ignition to start combustion.
How Diesel Fuel Systems Work
Diesel engines use a different approach. Instead of spark plugs, diesel fuel systems rely on the heat generated by compressing air inside the engine cylinder to ignite the fuel. Diesel fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber at very high pressures, using a system called common rail or direct injection.
Key components of a diesel fuel system include:
- Fuel Tank
- High-Pressure Fuel Pump
- Fuel Filter and Water Separator
- Fuel Injectors (operating at very high pressure)
Diesel fuel systems operate under much higher pressure to atomize the thicker diesel fuel effectively. The system also includes additional filters to remove water and impurities, which diesel fuel is more prone to contain.
Key Differences Between Diesel and Gasoline Fuel Systems
| Aspect | Gasoline Fuel System | Diesel Fuel System |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Injection Pressure | Lower pressure (up to ~60 psi) | Very high pressure (up to 30,000+ psi) |
| Ignition Method | Spark ignition | Compression ignition |
| Fuel Injector Location | Intake manifold or combustion chamber | Directly into combustion chamber |
| Fuel Type | Gasoline (lighter, more volatile) | Diesel (heavier, oilier) |
| Fuel Filtration | Standard fuel filters | Additional water separators needed |
| Complexity | Less complex | More complex and robust |
Advantages of Diesel Fuel Systems
- Better fuel economy due to higher energy density of diesel fuel
- More torque and power at low RPMs, ideal for trucks and heavy-duty vehicles
- Longer engine life due to robust construction
Advantages of Gasoline Fuel Systems
- Generally quieter and smoother engine operation
- Lower initial vehicle cost
- Better suited for light-duty and passenger vehicles
Final Thoughts
Both diesel and gasoline fuel systems have their strengths and weaknesses, tailored to the demands of different types of vehicles and driving conditions. Whether you prefer diesel’s fuel efficiency and torque or gasoline’s smoothness and cost-effectiveness depends on your needs and preferences. Diesel vs. Gasoline Fuel Systems